Rapel River Basin, central Chile
Socio-Economic Development
The water resources of the river system are vital for the agricultural sector, mining activities, and the hydropower generation in the basin. Particularly the agricultural production is a key sector in the basin, accounting for 93% of the basins water consumption (Rojas et al. 2020).
Adminstration and Population
Chile is divided into 17 administrative regions, which are sub-divided into provinces and municipalities (Fernandez & Gironas et al., 2021). Around 88% of the Rapel’s drainage area stretches across the VI Region. Around 8.15% fall into the Región Metropolitana de Santiago, namely the Alhue Municipality in Melpilla Province.
The Rapel basin has a total population of 914,555 (in 2017), accounting for 5.2% of the national population. The population density is relatively low, with 55.8 inhabitants/km2. Furthermore, the O'Higgins region's inhabitants predominately reside in urban areas (ODEPA, 2018). In general, Chile is highly urbanized. Furthermore, the population of the Rapel Basin resides mainly around the regional capital Rancagua or the city of San Fernando in the South. The rural-urban ratio is 25.6-74.4% (INE, 2017).
Furthermore, around 6.5% of the population in the O'Higgins region consider themselves indigenous or of indigenous descent. Compared to the characteristics of the national population, the share of the indigenous population in the O'Higgins region is below the national average of 12.8% (INE, 2017).
Furthermore, around 6.5% of the population in the O'Higgins region are indigenous or of indigenous descent. The share of an indigenous population in the O'Higgins region is below the national average of 12.8% (INE, 2017).
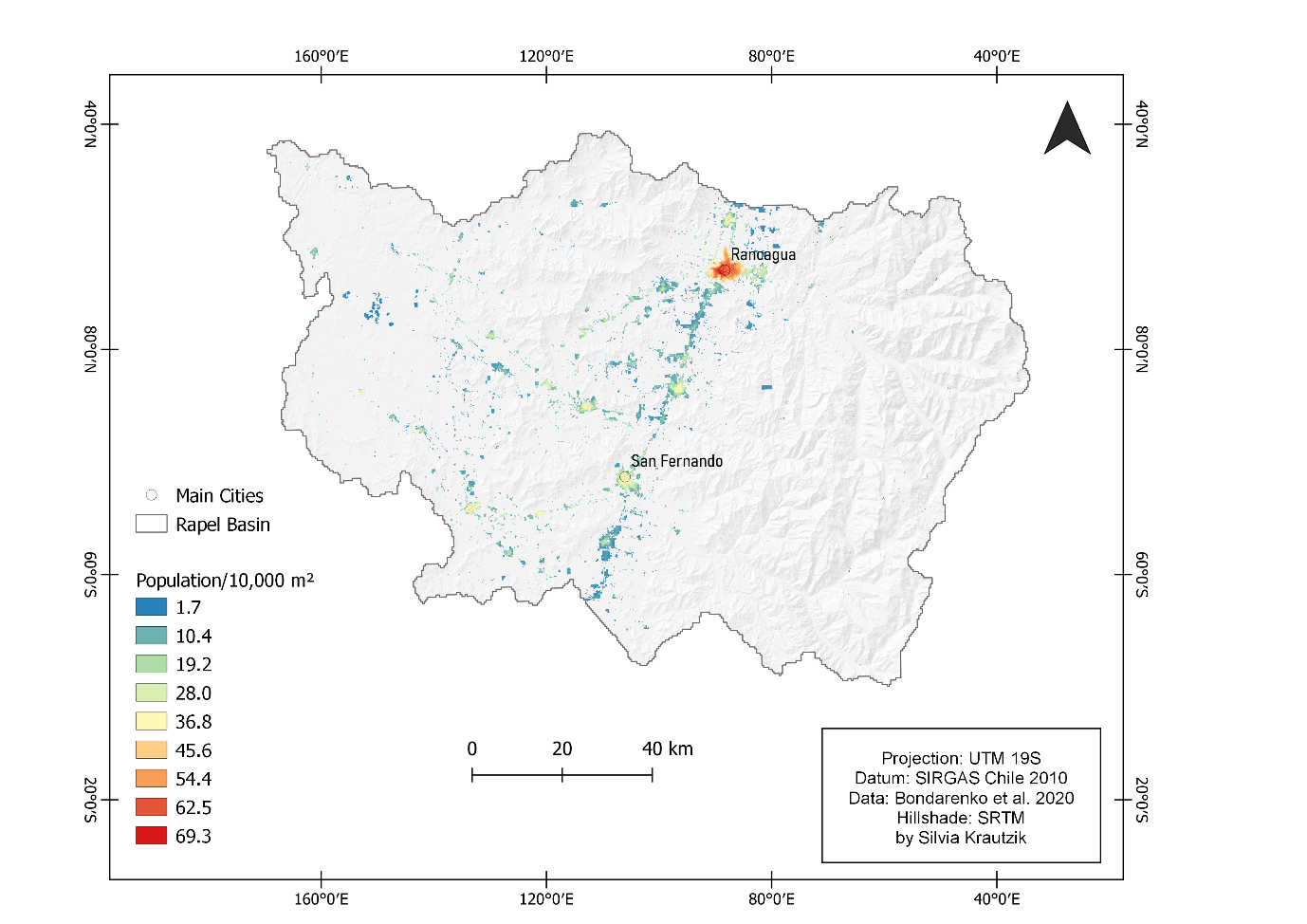
Figure 7: Spatial distribution of the population in the Rapel Basin, Chile (based on Bondarenko et al., 2020).
Economic Sectors
The region's main economic sectors are agriculture and mining, with a regional GDP of 15% and 19%, respectively (ODEPA, 2019).
Agricultural activity is central to the economy of O ́Higgins and for Chile in general (ODEPA, 2019). The agricultural sector of the O ́Higgins region employs 29.07% of the local labor (CONICYT, 2010).
The most important mining company is "El Teniente". The company operates a large copper mine in the Andes mountains, located 2,800 meters above the sea in the upper basin of the Cachapoal river (DGA, 2004).
Regional Household Income
The average income of a household in 2017 was 697,586 Chilean Pesos (1,074 USD) in the O'Higgins region. Compared to other regions in Chile, the O'Higgins region has one of the lower household incomes. For instance, the region Ñuble has the lowest national income level with 607,345 (935 USD) pesos. In comparison, Antofagasta has the highest monthly income level with 1,120,899 pesos (1,726 USD) (Ministderio de Desarollo Social y Familia, 2018).
Despite fast economic growth and significant improvements in the health, education, and economic sectors, relatively high poverty rates remain a central concern. In 2015, around 13.7% of the population in the O'Higgins region lived in poverty, and 3.8% lived in extreme poverty. The share of people living in poverty was slightly higher in rural areas (ODEPA, 2018). The national poverty line was 192.62 USD per month in November 2015 (Ministderio de Desarollo Social y Familia, 2018).
References:
BONDARENKO, M.; NIEVES, J. J.; STEVENS, F. R.; GAUGHAN, A. E., TATEM, A.; SORICHETTA, A. (2020) Random Forests population modelling R scripts, version 0.1.0. University of Southampton: Southampton, UK, doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.i5258/SOTON/WP00665.
DGA (2004): Diagnostico y clasificacion de los cursos y cuerpos de agua segun objetivos de calidad: Cuenca del Rio Rapel’.
Fernandez & Gironas et al. (2021): Droughts. In: Fernández, B.; Gironás, J. (eds.): Water Resources of Chile, Vol. 8,pp.173-187.
Ministderio de Desarollo Social y Familia (2018): Informe de Desarrollo Social 2018. Available at: https://www.desarrollosocialyfamilia.gob.cl/storage/docs/Informe_de_Desarrollo_Social _2018.pdf [accessed 26.07.2021].
INE (2017): Síntesis resultados Censo 2017. Junio/2018. Available at: https://www.ine.cl/docs/default-source/censo-de-poblacion-y-vivienda/publicaciones-y-anuarios/2017/publicación-de-resultados/sintesis-de-resultados-censo2017.pdf?sfvrsn=1b2dfb06_6 [Accessed 26.07.2021].
Rojas, R.; Bennison, G.; Gálvez, V.; Claro, E.; Castelblanco, G. (2020): Advancing Collaborative Water Governance: Unravelling Stakeholders’ Relationships and Influences in Contentious River Basins. In: Water, Vol.12(2020), pp. 1-25, doi:10.3390/w12123316
ODEPA (2018): Región del Libertador Bernardo O’Higgins Informe Regional. Available at: https://www.odepa.gob.cl/wp- content/uploads/2018/03/OHiggins.pdf [Accessed 26.07.2021].
ODEPA (2019): Región del Libertador Bernardo O’Higgins Informe Regional. Available at: https://www.odepa.gob.cl/wp- content/uploads/2019/07/OHiggins.pdf [Accessed 26.07.2021].

